Security researchers at Sekoia.io have uncovered a sophisticated cyberattack campaign orchestrated by APT28, the notorious Russian state-sponsored threat actor, targeting Ukrainian military personnel with weaponized Office documents that deliver advanced malware frameworks including BeardShell and Covenant modules.
The operation represents a significant evolution in APT28’s tactics, leveraging legitimate cloud infrastructure and novel obfuscation techniques to maintain persistent access while evading detection mechanisms.
The infection chain begins with malicious Office documents distributed through Signal Desktop, a platform APT28 deliberately chose because it lacks the Mark of the Web (MOTW) security mechanism that typically prevents macro execution in files from untrusted sources.


This technical gap allows embedded macros to run without triggering Microsoft Office’s standard security warnings, unlike documents downloaded from web browsers or received through email clients like Outlook.
The attackers impersonate colleagues or superiors in private Signal chats, creating false urgency by referencing compensation decisions and threatening legal action to manipulate targets into opening the malicious documents.
The lure documents themselves are carefully crafted to appear legitimate, featuring authentic Ukrainian military administrative forms including personnel evaluations, medical compensation requests, and drone delivery receipts.
This targeting strategy suggests APT28’s operational focus extends to gathering intelligence on frontline combatants, wounded personnel, unit assignments, and equipment supply chains within the Ukrainian military theater.
Sekoia researchers accessed these compromised accounts and discovered 115 files across multiple folders, with 42 unique partial GUIDs indicating at least 42 different compromised hosts, with the earliest infection dating to December 3, 2024.
Steganographic Payload Delivery
Once a victim enables macros, the Visual Basic script embedded in the Office document initiates a complex multi-stage infection process.
The macro first verifies the Windows operating system and VBA version, then switches the document to Print Layout view while deobfuscating hidden data by replacing character pairs.
The script establishes persistence by adding a registry entry that hijacks the Windows Printer COM server, causing the malicious DLL to load automatically whenever explorer.exe starts.


The infection chain drops two critical files: prnfldr.dll in C:\ProgramData\ and windows.png in the user’s AppData\Local directory.
The DLL functions as a proxy for the legitimate Windows printer library while secretly spawning a thread that extracts a shellcode payload hidden within the PNG file using steganographic techniques.
The malware reads the least significant bit of each pixel’s RGBA values to reconstruct an AES-encrypted blob containing the next stage shellcode.
The extracted shellcode initializes the Common Language Runtime environment to load a .NET executable identified as the HTTP Grunt Stager component of the Covenant framework, an open-source red team tool.
Afterwards, the array is loaded into the AppDomain via the AppDomain->Load_3 function, and its entry point is obtained using the _Assembly::get_EntryPoint function.


APT28 has customized this framework with a novel C2Bridge implementation that uses the Koofr cloud storage service API for command and control communications instead of traditional network protocols.
This approach allows the malware to upload reconnaissance data and download additional payloads through legitimate cloud infrastructure, making detection significantly more difficult.
During execution, the Covenant module connects to hardcoded Koofr accounts using embedded credentials and creates a directory structure for file-based communications.
The implant performs hybrid encryption for secure key exchange, then polls the cloud storage for new “Tasks” to execute, including screenshot capture, ARP scans, IP information requests, traceroute operations, and process enumeration.
PowerShell Execution Capabilities
According to CERT-UA’s analysis confirmed by Sekoia, the Covenant framework downloads additional components including PlaySndSrv.dll and sample-03.wav, which extract and execute BeardShell, a C++ backdoor that uses the icedrive cloud storage service as its command and control channel.


BeardShell generates a unique identifier for each infected host by hashing hardware profile GUIDs, computer names, domain names, usernames, and workstation names using the FNV4 algorithm.
The malware executes the SystemInfo command on startup and uploads results to icedrive, then polls its designated directory every four hours for operator-uploaded command files.
BeardShell implements seven distinct commands that enable operators to create PowerShell instances, execute commands and scripts, monitor execution status, and manage multiple sessions simultaneously.
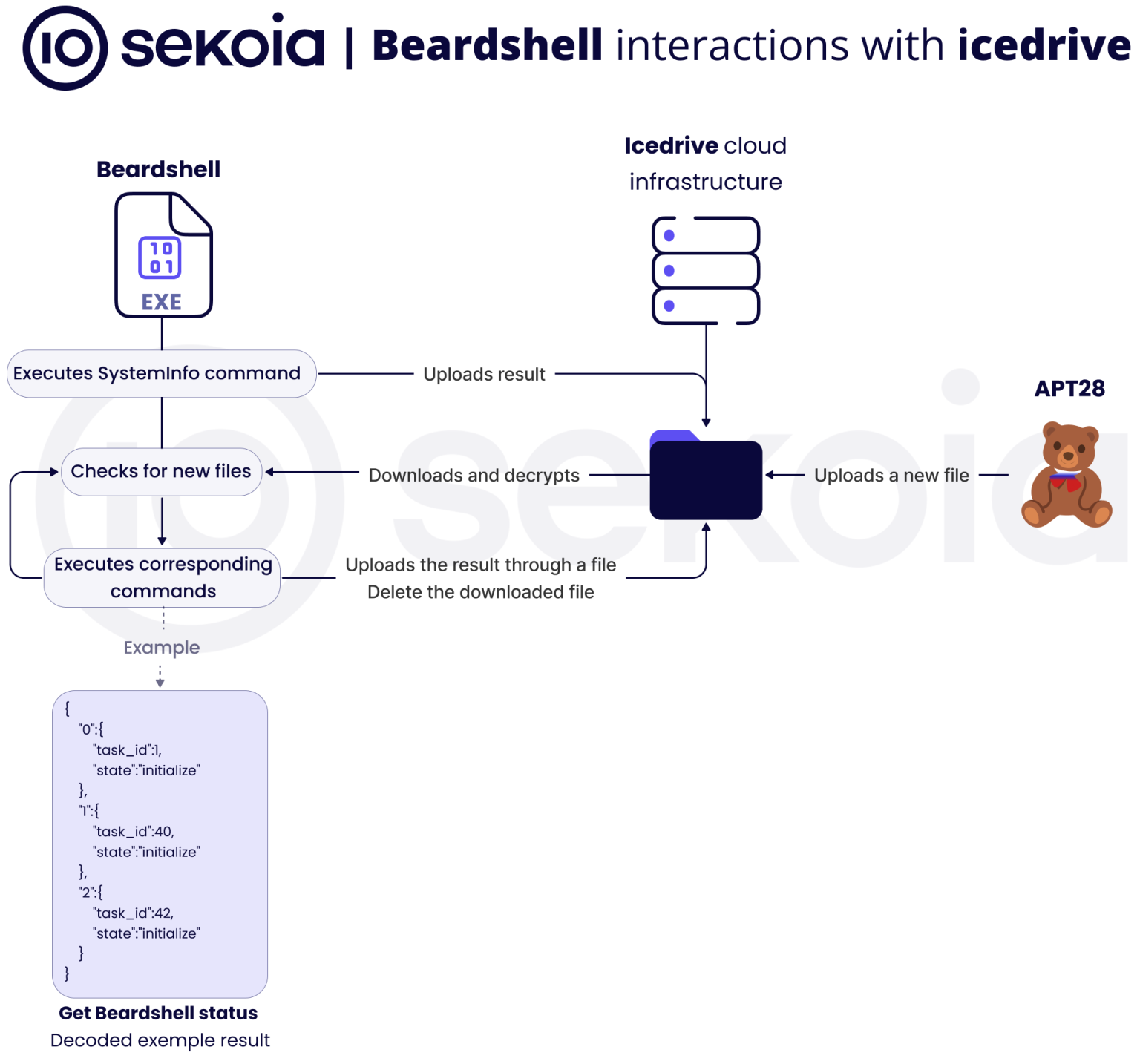

To evade detection, uploaded files are encrypted using the ChaCha20-Poly1305 algorithm and disguised with image file headers and extensions including BMP, GIF, JPEG, PNG, and TIFF.
APT28, also known by at least 28 aliases including Sofacy, Fancy Bear, BlueDelta, Forest Blizzard, and TAG-110, is attributed by Western intelligence agencies to Russia’s General Staff Main Intelligence Directorate (GRU), specifically the 85th Main Special Service Centre of Military Unit 26165.
Throughout 2025, the group has been the subject of multiple reports including a joint advisory from 21 international partners and analysis by France’s ANSSI.
The campaign demonstrates significant technical advancement over previous APT28 operations, integrating open-source offensive security tools with third-party cloud services for covert communications.
The use of steganography to embed payloads inside PNG files represents a novel obfuscation method not previously documented in APT28 activity.
Sekoia’s Threat Detection and Response team confirmed that in August 2025, APT28 reused this infection chain with a weaponized Excel document targeting the Filen cloud environment, indicating the group continues to adapt and recycle these sophisticated techniques.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates and Set GBH as a Preferred Source in Google.



